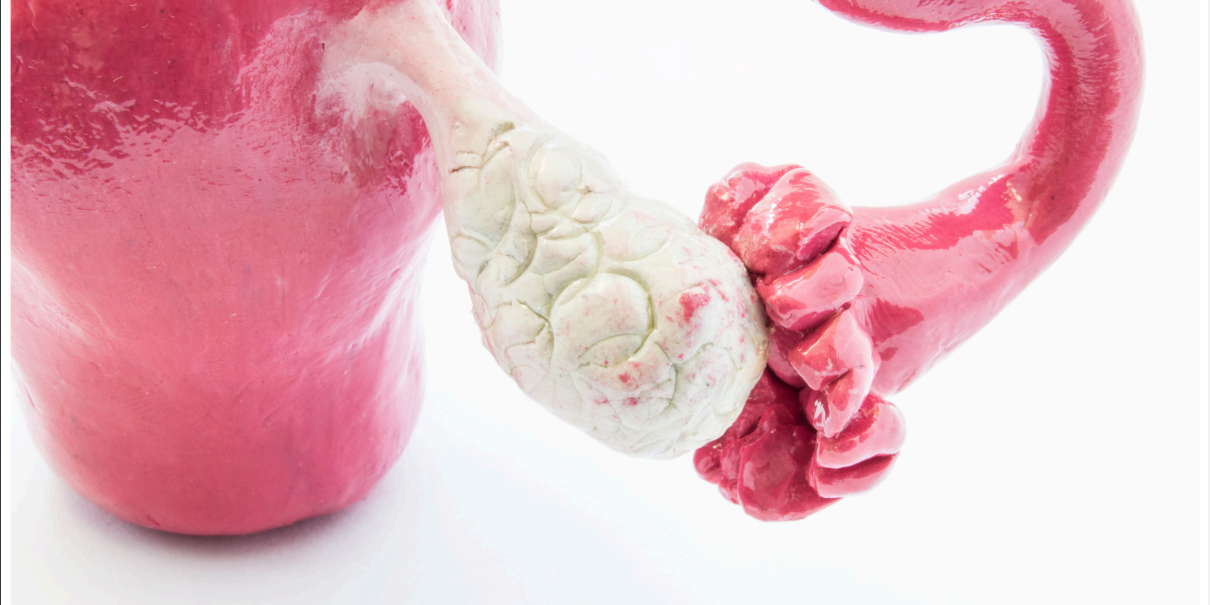
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder that specifically targets the ovaries, the essential organs for egg development in females. This condition is prevalent among about 1 in 10 women of reproductive age, making it a leading factor in infertility. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a syndrome characterized by cysts in the ovaries, high levels of male hormones, and irregular or skipped periods. The term “polycystic” refers to the presence of multiple small, fluid-filled sacs within the ovaries. These sacs, which are essentially follicles containing immature eggs, do not mature adequately to initiate ovulation. As a result, levels of estrogen, progesterone, FSH, and LH are altered in PCOS, with decreased progesterone levels and increased androgen levels. The excess male hormones disrupt the menstrual cycle, resulting in fewer periods for women with PCOS.
Symptoms of PCOS
Polycystic ovary syndrome is not classified as a disease, but rather as a collection of symptoms. The presentation of these symptoms may differ among individuals. However, the primary indicators of PCOS typically involve missed, irregular, infrequent, or prolonged menstrual cycles. Other signs and symptoms include: Acne, darkened skin, excess face and body hair, hair loss, mood changes, oily skin, ovarian cyst, pain, skin tags, and weight gain. In some cases, PCOS may not exhibit any noticeable symptoms or only mild ones that are easily overlooked. Given the overlap of symptoms with other menstrual disorders, arriving at a PCOS diagnosis may involve a lengthy process.
PCOS Treatment
There is no definitive cure for PCOS. The medical treatments recommended by your physician to manage your symptoms will be influenced by your desire to conceive. It is imperative to have a conversation with your doctor about this, as specific medications may have adverse effects on a developing fetus. Your physician may prescribe:
- Acne Medications
- Androgen blockers
- Hormonal birth control
- Insulin- sensitizing medications
- Progestin Therapy
- Medications to help you ovulate
When to see a doctor
Should you find yourself in a situation where you have missed periods without being pregnant, are noticing symptoms of PCOS like unwanted hair growth, have been unsuccessful in conceiving for more than a year, or are displaying signs of diabetes such as increased thirst or unexplained weight loss, it is important to schedule an appointment with your healthcare provider. For individuals with PCOS, it is recommended to schedule regular appointments with your primary care doctor. Regular tests should be conducted to monitor for potential complications such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and other related conditions.
Find Gynecologist for PCOS
If you need additional information or are concerned about PCOS please contact us at 346-585-4077